In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and improve efficiency. Three popular technologies leading this transformation are Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Workflow Automation, and AI Agents. While they may sound similar, each serves a distinct purpose and brings unique value to the table.
Let’s dive into the differences, strengths, and best use cases for these solutions. We will take a simple use case of, you have received a Payable invoice in your inbox and you need to handle, record and pay it – if it passes all the tests. We will contrast the effort needed, the results and limitations of each technology as they handle the use case.
What is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software bots to mimic repetitive human actions within digital systems. It is particularly effective for rule-based tasks that require interacting with multiple applications without human intervention. Known vendors in this space are Automation Anywhere, UI Path etc.

Key Features:
- Automates manual, repetitive tasks.
- Works across legacy systems without API integration.
- Reduces human error and increases productivity.
Use Cases:
- Data entry and validation.
- Invoice processing.
- Employee onboarding.
RPA for Invoice Processing
In the context of end-end invoice processing, one needs to create multiple RPA bots to handle the complete process. These bots could be attended or unattended bots. Here’s how the structure would look like in the RPA world:
- Invoice lookup and scanning (Bot 1)
- The bot looks for an “alert” to start looking for incoming/new invoices (emails, shared folders, EDI etc.)
- It uses OCR to read and structure the data based on the different fields.
- While it can write to a data repository, the data still is unverified to be processed. So most likely the structured data is “handed off” for downstream use, possibly like an XL/JSON file.
- 3-Way Matching (Bot 2)
- The second bot picks up the structured data (from Bot 1) and prepares to do a 3-way match. The execution of this bot has to timed with the completion of Bot 1, and even a precursory check to ensure Bot1 output is valid. This is where RPA can get overly complicated.
- The 3-way matching is done by comparing against the Purchase Order, and Goods Receipt Note (say).
- Business rules are applied to validate the invoicing entries matches, if not discrepancies are “notified”. The notification and subsequent approval is another shortcoming of RPA – it doesn’t know how to “ping” the Approver.
- The data is now recorded, for further downstream processing.
- Posting and Logging (Bot 3)
- Upon successful validation, the third bot logs into the company’s ERP system (e.g., SAP, Oracle) and posts the invoice entry.
- It can additionally calculate any tax or discounts, that need to be applied before logging the entry.
- After posting, a confirmation number or transaction ID is retrieved. All of the data is included in the Final log, that is generated for audit purposes, and the information is stored for future reference
What is Workflow Automation?
Workflow Automation involves designing and managing sequences of tasks or processes using software. Workflow automation platforms come in two flavors – No-Code & Low-Code. Read here to understand the key differences between the two flavors. Unlike RPA, it manages end-to-end business processes and often requires human input for decision-making steps (think Approvals). Known vendors in this space are Kissflow, Zapier, Make, VorkFlow etc.
Key Features:
- Streamlines complex business processes.
- Provides visibility into workflows.
- Supports collaboration across departments.
Use Cases:
- Approval workflows (e.g., purchase orders, expense approvals).
- Document management and routing.
- Customer onboarding.
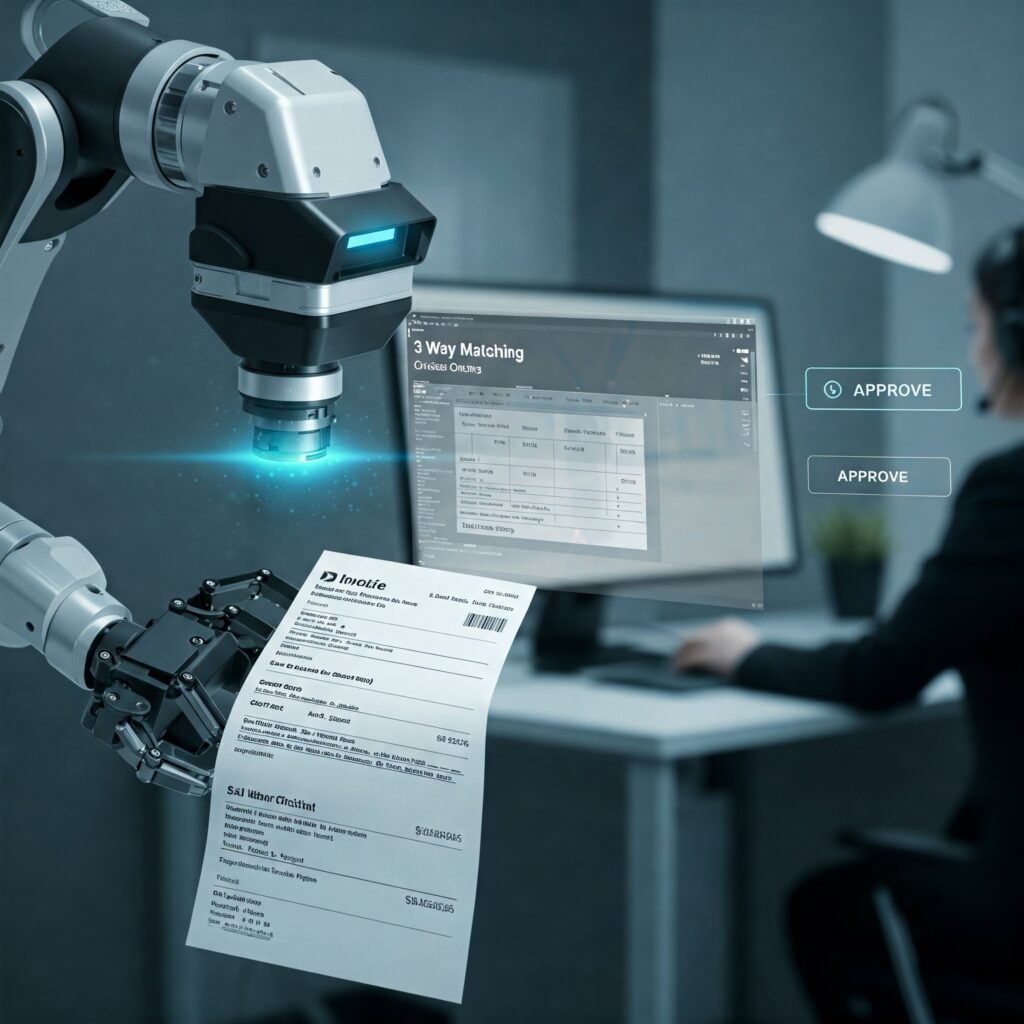

Workflow Automation for Invoice Processing
In the context of invoice processing, a no-code workflow automation platforms like VorkFlow enables business users to build a data flow diagram detailing how the invoice processing needs to be happen. The data flow diagram can further be modelled into an executable workflow, using drag-drop interfaces and calling one or more external API’s. Here’s how a workflow automation platforms can handle invoice processing.
- Invoice Ingestion and Capture
- Invoices can be ingested from multiple sources (email, portals, EDI, scanned documents) using integrations or APIs. This negates the need for any manual intervention.
- The workflow triggers an Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) module that uses OCR or AI to extract data. If the scan was unsuccessful or there were some failure, the workflow stops and a notification email is sent to the appropriate approver. The workflow waits for the approval to either restart or proceed with previous error. This human-centric approval is what differentiates workflow automation from RPA.
- Just like the RPA bot, all data elements are extracted, cleansed, structured and assembled for the next step.
- Worth noting that, if invoice format changes, the workflow automation tools seamless handles the change
- 3-Way Matching
- The workflow uses pre-built connectors to access data from the ERP system and pull relevant POs and GRNs.
- The 3-Way matching is performed, just like an RPA bot. Any discrepancies associated with the matching process are flagged automatically. These include invoices with no PO, or invoices where the amount differs from the PO.
- It is possible to enable real-time validation with visibility into why an invoice failed the match. Custom business rules can be embedded within the workflow, to ensure compliance without manual intervention. VorkFlow is unique compared to its competition, where any workflow can be costomized per business rules.
- Exception Management with Human-in-the-Loop
- If a mismatch occurs or approval is needed, the workflow triggers a human task using a simple UI.
- The approver receives an actionable dashboard with highlighted exceptions, suggested resolutions, and supporting documents.
- Approvers can approve, reject, or escalate with comments.
- The workflow tracks every decision for audit purposes.
- Automated Posting and Notifications
- Once approved, the workflow automatically posts the invoice to the ERP system via integration.
- Payment terms, taxes, and discounts are applied per configured rules.
- Status notifications are sent to stakeholders and vendors through email or in-app alerts.
- Analytics and Continuous Improvement
- The workflow automation platform tracks KPIs like processing time, exception rates, and approver delays.
- AI-powered insights recommend process improvements, such as identifying frequent vendor issues or suggesting rule adjustments
- Users can generate reports and dashboards for operational visibility.
What are AI Agents?
AI Agents are intelligent systems capable of making decisions, learning from data, and performing tasks autonomously. They use machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and predictive analytics to perform complex problem-solving tasks.
Key Features:
- Learns and adapts over time.
- Understands unstructured data.
- Makes data-driven decisions.
Use Cases:
- Customer service chatbots.
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
- Personalized recommendations.
AI Agents for Invoice Processing
In the context of invoice processing, an AI agent could take the process a step further by adding intelligence, learning capabilities, and proactive decision-making. Here’s how an AI agent would enhance the workflow beyond traditional automation:
- Intelligent Data Extraction and Understanding
- While a workflow automation bot might extract structured data using OCR (Optical Character Recognition), an AI agent could analyze unstructured or semi-structured data, such as invoice comments, handwritten notes, or different invoice formats.
- The AI agent can detect anomalies, identify missing fields, and infer context using natural language processing (NLP).
- Contextual Decision-Making
- If there are discrepancies during the 3-way match (invoice, purchase order, and goods receipt), an AI agent can evaluate past transactions, supplier reliability, and purchasing trends to recommend whether the invoice should be flagged, approved with adjustments, or sent for further investigation.
- It could also provide reasons and confidence scores for its recommendations.
- Proactive Risk Management
- AI agents can detect fraud patterns or duplicate invoices by analyzing historical data and applying anomaly detection algorithms.
- They can send real-time alerts and suggest corrective actions, minimizing financial risk.
- Learning and Continuous Improvement
- Unlike a bot that follows set rules, AI agents learn from past decisions and continuously improve their accuracy.
- For example, if an AI agent observes that specific invoice patterns are frequently approved despite minor discrepancies, it may adapt its decision-making to reduce unnecessary escalations.
- Supplier Management Insights
- AI agents can assess supplier performance, track payment delays, and provide actionable insights for negotiations or contract improvements.
- They might suggest early payment discounts or flag suppliers with inconsistent invoicing behaviors.
- Human Interaction Support
- When a human is needed for final approval, the AI agent can generate summarized insights and suggest the most likely decision based on historical data and current trends.
- It could also provide simulation models to show potential impacts of different decisions.
Key Differences at a Glance
| Aspect | RPA | Workflow Automation | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Task automation | Process management | Decision-making and adaptation |
| Human Interaction | Minimal | Moderate | Contextual understanding and decision-making |
| Complexity | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High | High |
| Learning Capability | No | No | Yes |
| Use Case Focus | Repetitive, rule-based tasks | End-to-end process management | Adaptive, intelligent decision-making |
| Supportability | Very susceptible to break, requires redo in most cases | No Code automation workflows needs to be changed if the process is no longer relevant. | Depends on the intelligence baked into the AI model. Expensive to change. |
Which Solution is Right for You?
- Choose RPA if you need to automate repetitive, manual tasks with minimal complexity.
- Choose Workflow Automation for managing cross-functional business processes that require transparency and collaboration.
- Choose AI Agents when your operations involve complex decision-making, require predictive insights, or demand personalized user interactions.
In many cases, a combination of these technologies delivers the best results. For example, RPA can handle repetitive data entry, while workflow automation manages approvals, and AI agents provide data-driven insights to optimize processes.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of RPA, workflow automation, and AI agents helps businesses choose the right technology to meet their goals. RPA has its limitations, several. There is no doubt that AI is already helping many organizations improve operations, boost financial performance and deliver a better experience. However, business users are “weary yet hopeful” about the promise of AI. According to Experian Health’s State of Claims survey, the number of providers using automation and AI in revenue cycle management has halved from 62% in 2022 to 31% in 2024. So AI Agents for business automation is still in its infancy. At this time, no-code automation platforms are a great choice for many businesses. VorkFlow is a great option that is both integration-centric and human-centric. It’s also the fastest compared to our competition.
Ready to move from Archaic RPA process?
Say goodbye to rigid bots and hello to flexible, adaptable automation.
Explore the possibilities of intelligent automation and see the difference. Take control of your automation journey with intuitive, powerful tools.
See a live demo and witness the evolution of automation first hand. Let us show you how we migrate your RPA — within days.
